-
Accounting Advisory
Our accounting advisory team help businesses meet their complex financial reporting requirements. The team can support in applying new financial reporting standards, IFRS/ US GAAP conversions, financial statement preparation, consolidation and more.
-
Payroll
Our team can handle your payroll processing needs to help you reduce cost and saves time so that you can focus on your core competencies
-
Managed accounting and bookkeeping
Outsourcing the financial reporting function is a growing trend among middle market and startup companies, as it provides a cost-effective way to improve the finance and accounting function. Our team can help with financial statement preparation, consolidation and technical on-call advisory.
-
Accounting Advisory
Our team helps companies keep up with changes to international and domestic financial reporting standards so that they have the right accounting policies and operating models to prevent unexpected surprises.
-
Crypto Accounting Advisory Service
Our team can help you explore appropriate accounting treatment for accounting for holdings in cryptocurrencies, issuance of cryptocurrencies and other crypto/blockchain related accounting issues.
-
ESG Reporting and Accounting
As part of our ESG and Sustainability Services, our team will work with you on various aspects of ESG accounting and ESG reporting so that your business can be pursue a sustainable future.
-
Expected Credit Loss
Our team of ECL modelling specialists combine help clients implement provisioning methodology and processes which are right for them.
-
Finance Transformation
Our Finance Transformation services are designed to challenge the status quo and enable your finance team to play a more strategic role in the organisation.
-
Managed Accounting and Bookkeeping Services
Outsourcing the financial reporting function is a growing trend among middle market and startup companies, as it provides a cost-effective way to improve the finance and accounting function. Our team can help with financial statement preparation, consolidation and technical on-call advisory.
-
Business Tax Advisory
Our business tax team can help you navigate the international tax landscape, grow through mergers and acquisitions, or plan an exit strategy.
-
Corporate Finance
Our corporate finance team helps companies with capital raising, mergers and acquisitions, private equity, strategic joint ventures, special situations and more.
-
Financial Due Diligence
From exploring the strategic options available to businesses and shareholders through to advising and project managing the chosen solution, our team provide a truly integrated offering
-
Valuations
Our valuation specialists blend technical expertise with a pragmatic outlook to deliver support in financial reporting, transactions, restructuring, and disputes.

-
Sustainability with the ARC framework
Backed by the CTC Grant, businesses can tap on the ARC Framework to gain access to sustainability internally, transform business processes, redefine job roles for workers, and enhance productivity. Companies can leverage this grant to drive workforce and enterprise transformation.

-
Business Tax Advisory
Our business tax team can help you navigate the international tax landscape, grow through mergers and acquisitions, or plan an exit strategy.
-
Corporate Tax Compliance
Our corporate tax teams prepare corporate tax files and ruling requests, support you with deferrals, accounting procedures and realise tax benefits.
-
Tax Governance
Our Tax Governance Services are designed to assist organisations in establishing effective tax governance practices, enabling them to navigate the intricate tax environment with confidence.
-
Goods and Services Tax
Our GST team supports organisations throughout the entire business life-cycle. We can help with GST registration, compliance, risk management, scheme renewals, transaction advisory and more.
-
Transfer Pricing
Our Transfer Pricing team advises clients on their transfer pricing matters on and end-to-end basis right from the designing of policies, to assistance with annual compliance and assistance with defense against the claims of competing tax authorities.
-
Employer Solutions
Our Employer Solutions team helps businesses remain compliant in Singapore as well as globally as a result of their employees' movements. From running local payroll, to implementing a global equity reward scheme or even advising on the structure of employees’ cross-border travel.
-
Private Client Services
Our private client services team provides a comprehensive cross section of advisory services to high net worth individuals and corporate executives, allowing such individuals to concentrate on their business interests.
-
Welfare and benefits
We believe that a thriving team is one where each individual feels valued, fulfilled, and empowered to achieve their best. Our welfare and benefits aim to care for your wellbeing both professionally and personally.
-
Career development
We want to help our people learn and grow in the right direction. We seek to provide each individual with the right opportunities and support to enable them to achieve their best.
IAS 36 ‘Impairment of Assets’ provides the core principles when assessing if an asset should be impaired. However, due to the complex nature of the guidance, the requirements of IAS 36 can be challenging to apply in practice.
The articles in our ‘Insights into IAS 36’ series have been written to assist preparers of financial statements and those charged with the governance of reporting entities understand the requirements set out in IAS 36, and revisit some areas where confusion has been seen in practice. This article, Scope and structure of IAS 36, looks at the scope of the impairment review (ie the types of assets that are included) and how it is structured (ie the level at which assets are reviewed).
In this article
Assets must be reviewed for impairment at the lowest level possible – sometimes this is at the individual asset level but more often assets are allocated to a cash generating unit (CGU) for impairment review purposes. Further, goodwill and corporate assets will need to be allocated to a CGU or groups of CGUs.
This article covers the following two steps of any impairment review:
- Step 1: Identify assets within the scope of IAS 36
- Step 2: Determine the structure of the impairment review.
The remaining steps will be considered in subsequent articles. For a summary of the steps in applying IAS 36, refer to our article ‘Insights into IAS 36 – Overview of the Standard’.
Step 1: Identify assets within the scope of IAS 36
IAS 36 must be applied in accounting for the impairment of all assets, unless they are specifically excluded from its scope. The scope exceptions cover assets for which the requirements of other IFRS render an IAS 36-based impairment review irrelevant or unnecessary (eg – IAS 2 ‘Inventories’ requires that inventory be written down to its net realisable value if lower than cost, so inventory is explicitly excluded from the scope of IAS 36). The table below summarises IAS 36’s scope.
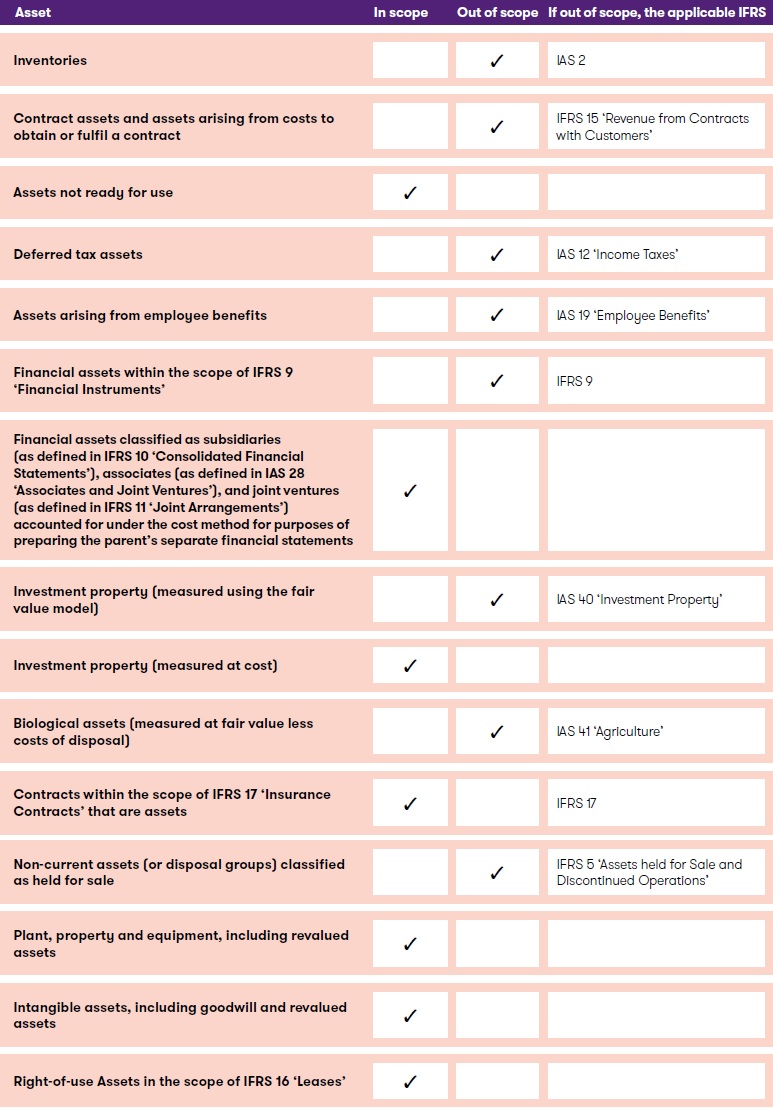
Other assets not specifically excluded in the above table are within the scope of IAS 36.
Step 2: Determine the structure of the impairment review
Once an entity has confirmed the assets in question are within the scope of IAS 36, the next step is to determine whether the asset will be reviewed for impairment individually or as part of a larger group of assets or CGUs (in other words, the structure of the impairment review for purposes of applying IAS 36).
When possible, IAS 36 should be applied at the individual asset level. This will be possible only when:
- the asset generates cash inflows that are largely independent of those from other assets or groups of assets) or
- the asset’s value in use (VIU) can be estimated to be close to fair value less costs of disposal (FVLCOD) and FVLCOD can be measured.
The below flowchart describes the assessment to determine the structure of the impairment review:
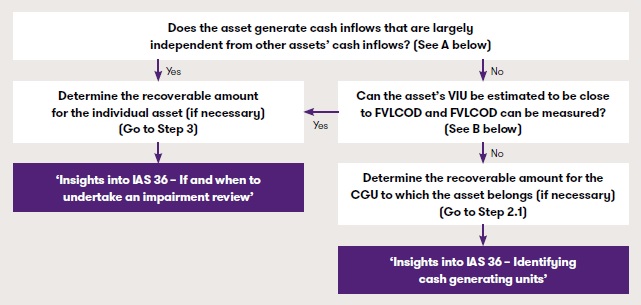
A. Cash inflows that are largely independent
When determining if an asset generates cash inflows that are largely independent of the cash inflows from other assets (or groups of assets), an entity considers various factors including:
- how management monitors the entity’s operation (such as by product lines, businesses, individual locations, districts or regional areas), or
- how management makes decisions about continuing or disposing of the entity’s assets and operations.
The following example shows how this guidance may be applied in practice.
A television network owns 50 TV programmes of which 20 were purchased and 30 were self-created. The network recognises each purchased programme as an intangible asset at the price paid while it expenses the cost of developing new and maintaining old programmes as incurred. Cash inflows are generated from licensing of broadcasting rights to other networks and advertising sales and are identifiable for each programme. The network manages programmes by customer segments. Programmes within the same customer segment affect to some extent the level of advertising income generated by other programmes in the segment. Management often abandons older programmes before the end of their economic lives to replace them with newer programmes targeted to the same customer segment.
In this case, the cash inflows from each TV programme are largely independent. Even though the level of licensing and advertising income for a programme is influenced by the other programmes in the customer segment, cash inflows are identifiable for each individual programme. In addition, although programmes are managed by customer segments, decisions to abandon programmes are made on an individual basis.
IAS 36’s guidance on whether recoverable amount can be determined for an individual asset specifically refers to cash inflows, not net cash flows or cash outflows. Accordingly, if an asset’s cash inflows are largely independent but some of the related costs are interdependent with other assets, recoverable amount must still be determined at the individual asset level (if necessary).
B. VIU can be estimated to be close to FVLCOD and FVLCOD can be measured
From the above flowchart, if an entity determines the asset in question does not generate cash inflows that are largely independent of those from other assets, it should assess if the asset’s VIU can be estimated to be close to FVLCOD. The VIU of an asset may be assessed as close to or less than FVLCOD when the asset is no longer in use, or soon to be replaced or abandoned, such that the estimated future cash flows from continuing use of the asset are negligible (eg, where an entity holds a brand solely for defensive purposes). Further, VIU may be assessed to be close to FVLCOD in the limited circumstances when the entity’s estimated cash flows from using the asset are consistent with the cash flows market participants would expect to generate, and costs of disposal are not material (ie when there are no entity-specific advantages or disadvantages, including tax-related factors).
When VIU can be estimated to be close to FVLCOD, the entity will determine the recoverable amount for the individual asset (the asset will not be included in a CGU for impairment assessment purposes) and any impairment is recognised immediately at the individual asset level.
Finally, when there is no reason to believe that VIU materially exceeds FVLCOD, IAS 36 allows an entity to estimate FVLCOD only for purposes of determining the recoverable amount.
The following example illustrates one application of this guidance.
A mining entity owns a private railway to support its mining activities. The private railway does not generate cash inflows that are largely independent of the cash inflows from other assets of the mine. The costs of disposal of the private railway are expected to be high.
It is not possible to estimate the recoverable amount of the private railway on a standalone basis because its VIU cannot be determined standalone and is probably different from the amount it would receive on disposal (in part due to the high costs associated with disposal). Therefore, the entity estimates the recoverable amount of the CGU to which the private railway belongs, which could be the mine as a whole.
Most assets generate cash inflows only in combination with other assets as part of a larger CGU. It is not possible to calculate a recoverable amount for most individual assets that are held for continuing use.
Management must then identify the CGU to which an asset belongs to determine if quantitative impairment testing is required. The relevant guidance and application issues associated with this process are discussed in our article ‘Insights into IAS 36 – Identifying cash generating units’.



